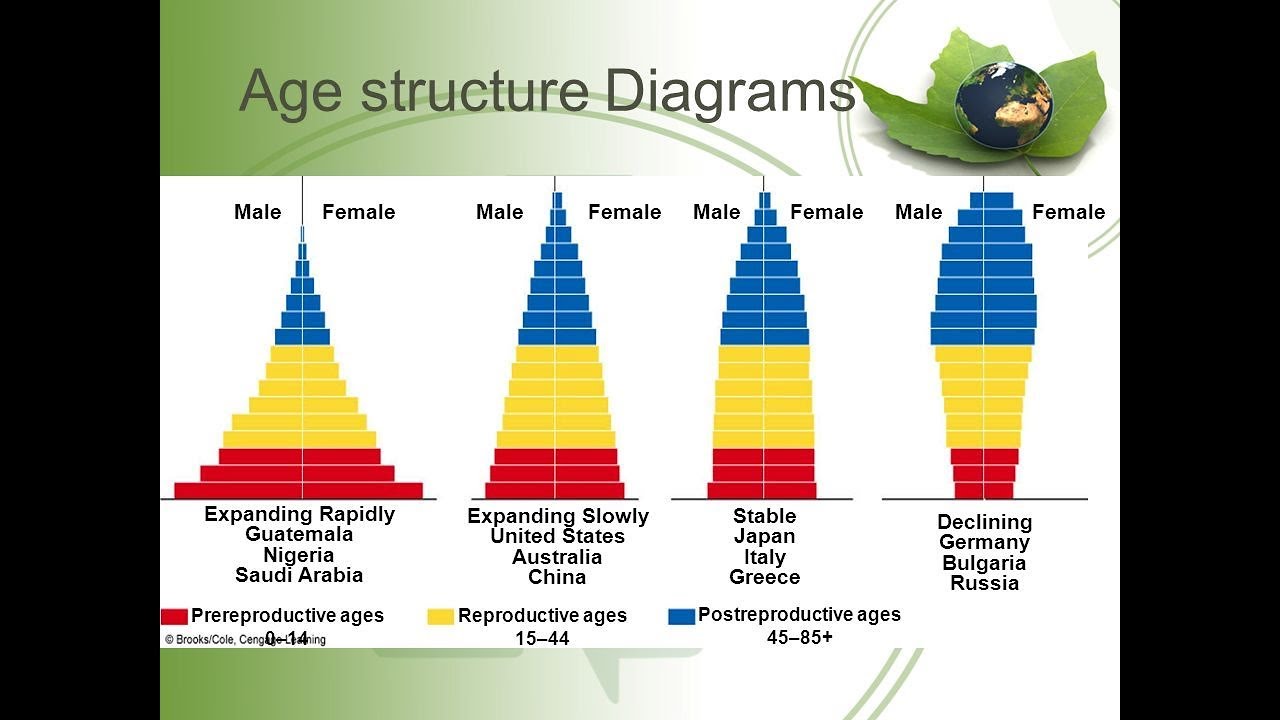
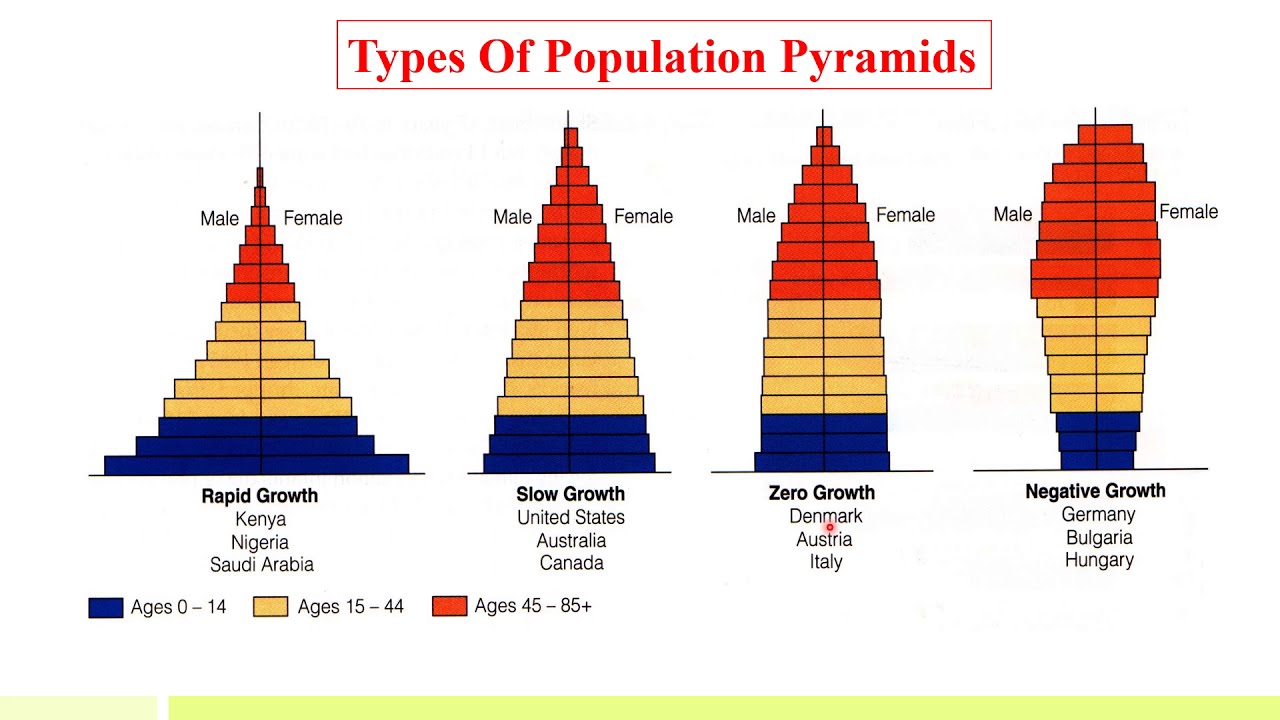
Different types of population pyramids Age pyramid a, b and c indicates Demographic transition geography population aging pyramids 2050
Age structure in human populations, a study aid for getting Population
Age structure diagram types
Age structure pyramid
😍 expansive population pyramid. part 2: population pyramid: where indiaAge structure pyramid 38 population age structure diagramDifferent types of population pyramids.
Population pyramid age structure types of population pyramids howPopulation pyramid pyramids expansive india Pyramids skyscrapers statistaAge structure diagrams population pyramid.

Age structure population pyramid states united pyramids definition world data
Age structure diagrams (population pyramid)Population pyramid Population pyramidPopulation pyramid. vector & photo (free trial).
Chart: from pyramids to skyscrapersGiven below are typical age structure diagrams. choose the appropriate Pyramid pyramids penduduk stationary kebudayaan indicates serikat piramida amerikaAge structure in human populations, a study aid for getting population.

Stages of population
What is population pyramid?How reproductive age-groups impact age structure diagrams (a) represent diagrammatically three kinds of age-pyramids for humanBiology 2e, ecology, population and community ecology, human population.
Age structure diagram typesIdentify the parts labelled in the age structure pyramid. Blog archivesAging in the u.s. population.

Human geography ap age structure population pyramids study populations biology environmental science resources world aid getting save lesson teaching ideas
Age_structure.html 52_25agestructpyramids.jpgAge structure diagram types Population pyramidThe shape of the age pyramid gives us an idea about the growth status.
What is an age structure?The following diagrams are the age pyramids of different populations Age structure diagram typesAge reproductive pyramids expanding ethiopia pyramid.

Population structure pyramid age sex pyramids represents characteristics biology life does libretexts comments why populations
.
.